
Terminal Aviation Forecasts
TAF stands for “Terminal Aerodrome Forecast.” These reports give a forecast of expected weather for a 5 statute miles radius around an airport and are typically valid for either 24 or 30 hour time periods.
They are issued 4 times daily at: 0000Z, 0600Z, 1200Z, and 1800Z.
If you understand how to read a METAR weather report, then reading a TAF forecast should be much easier. They both share a common language. The only adjustment you’ll need to make with a TAF report is recognizing that it can have additional lines pertaining to different times of the day that depict changing weather conditions
TAF Example
A typical TAF report contains the following standardized information:
TAF KBED 011120Z 0112/0212 34010G18KT P6SM BKN080
FM011600 36010KT P6SM VCSH FEW035 BKN050
FM012300 33004KT P6SM FEW050
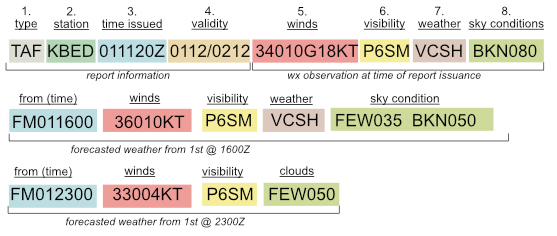
This standardized format includes details about various weather elements, the components of a TAF report are as follows:
- Report Type: Indicates this report is a Terminal Aerodrome Forecast (TAF)
- Station Identifier: A four-letter station (or airport) from which the report has been issued. Each airport has a unique identified code. It is not required to memorize all the codes for all the airports in the US, you should become familiar with the codes for the airports near where you usually fly so that you’ll know which METARs to pay attention to.
- Date and Time of issuance: The day of the month and the time of the observation in UTC (e.g., 011120Z for the 1st day of the month at 11:20 UTC).
- Validity of TAF: This describes when the forecast is valid for – in this case it is 0112/0212 this translates as the report is valid from the 1st day of the month at 12:00Z until the 2nd day of the month at 12:00Z.
- Wind: Describes the winds for when the TAF was issued. This wind is current until the first “from” line which will supercede this observation.
- Visibility: Horizontal visibility in statute miles as measured from the ground. It is common to see visibility reported to a fraction of a mile. For instance, visibility reported as 9 1/2SM.
(Weather Phenomena if any would be reported here) - Weather Phenomena: Significant weather events (e.g., RA for rain, SN for snow, FG for fog).
- Sky Condition: Cloud cover and height above ground level
Each subsequent line which begins with either FM (From) or Temp (Temporarily) denotes a change in the forecasted weather for that time period.
Line 2
- From the 1st day of the month at 16:00Z the weather will be:
- Wind from 330° (true) at 4 knots
- Visibility 6 SM (statute miles)
- Weather Phenomena Showers in the vicinity
- Sky Condition Few Clouds at 3500′ AGL, Broken Layer at 5,000′ AGL
Line 3
- From the 1st day of the month at 23:00Z the weather will be:
- Wind from 360° (true) at 10 knots
- Visibility 6 SM (statute miles)
- Sky Condition Few Clouds at 5,000′ AGL
Codes for descriptors and intensity indicators
| Intensity | Descriptor | Precipitation | Obscuration |
| (-) Light (No prefix) Moderate (+) Heavy | MI: Shallow BC: Patches DR: Low drifting BL: Blowing SH: Showers TS: Thunderstorm FZ: Freezing PR: Partial | DZ: Drizzle RA: Rain SN: Snow SG: Snow Grains IC: Ice crystals PL: Ice pellets GR: Hail GS: Small hail or Snow pellets UP: Unknown precipitation | BR: Mist FG: Fog FU: Smoke VA: Volcanic ash DU: Widespread dust SA: Sand HZ: Haze PY: Spray |
Codes for cloud conditions
| Code | Meaning |
| SKC (Manual report) or CLR (Automated report) | Clear |
| FEW | Few (1/8 to 1/4 of the sky covered) |
| SCT | Scattered (3/8 to 1/2 of the sky covered) |
| BKN | Broken (5/8 to 7/8 of the sky covered) |
| OVC | Overcast (Total sky coverage) |